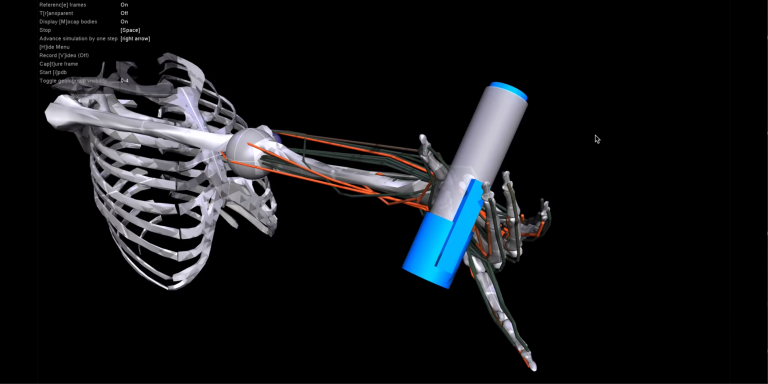
On May 23, Mark Zuckerberg announced that researchers from Meta’s AI Research Lab and the University of Twente’s Neuromechanical Modeling and Engineering Lab in the Netherlands, led by Professor Massimo Sartori, had collaborated to develop an open source framework called “MyoSuite,” which combines advanced musculoskeletal models with advanced AI. MyoSuite’s AI-powered digital models can learn to perform complex movements and interactions with assistive robots, which would require lengthy experiments on real human subjects. They titled their study ” Myosuite, A contact-rich simulation suite for Musculoskeletal motor control.
The motor behavior of an intelligent being is complex. Vikash Kumar and Vittorio Caggiano of Meta AI Research have teamed up with
Huawei Huang and Guillaume Durandau from the University of Twente, Enschede, The Netherlands to develop MyoSuite: a set of musculoskeletal models and tasks that allow the application of ML to solve biomechanical control problems. MyoSuite combines the two sides of intelligence: motor and neural.
Biomechanics
Biomechanics aims at studying the functions and properties of the human body movement, it is very useful to create equipments adapted to the human body (seats, desks, cars…), to improve the sports performances, in the health field…
However, human biomechanics is very complex and requires efficient coordination between the central nervous system, where decisions are synthesized by networks of billions of neurons, and the peripheral musculoskeletal system, which translates these intentions into actions.
Exploring musculoskeletal motor control with ML
ML algorithms are rarely used to explore complex motor control situations such as musculoskeletal control.
There are existing in silico frameworks that, like OpenSim, contain physiologically detailed musculoskeletal models, but they lack the ability to interact in a complex way with the physical world outside the agent’s body. According to the researchers, “these existing frameworks are neither integrated with complex, skillful motor tasks nor are they computationally efficient or scalable enough to meet the data requirements of ML algorithms. MyoSuite fills these gaps.”
The MyoSuite platform was designed to study the physiological details behind musculoskeletal motor control. It includes a comprehensive set of accurate musculoskeletal models that take into account musculoskeletal dynamics and its temporal interactions, such as muscle fatigue or sarcopenia, which affects humans around the age of 50, when muscle mass and strength decrease significantly, leading to, for example, gait disorders as well as daily behavioral tasks, injury rehabilitation and prosthetic/exoskeletal assistance.
MyoSuite’s musculoskeletal models are, according to the team, up to 4,000 times faster than other simulators in meeting the data requirements of modern ML algorithms.
Prof. Massimo Sartori states:
” This is all achieved by combining state-of-the-art musculoskeletal modeling with advanced artificial intelligence for motion behavior synthesis.”
Real-world applications
MyoSuite synthesizes behavior, but can also facilitate applications with real-world implications, such as rehabilitation, surgery, and shared autonomy assistive devices.
Using the example of a tendon tear, MyoSuite modeled tendon transfer, a common technique for recovering functionality from a torn tendon. It then simulated the outcome of a surgical procedure and the impact it will have on functional rehabilitation.
This research could have a significant impact for prosthetic development and post-trauma rehabilitation, as MyoSuite generated physiologically realistic movements, such as spinning a pen or manipulating Baoding balls, in great detail. The team has released it as open source and will soon launch MyoChallenge, a NeurIPS competition track where the ML community will be invited to participate in solving two of the most difficult dexterity challenges: reorienting the dice and rotating two Baoding balls simultaneously.
Article Sources:
MYOSUITE: A CONTACT-RICH SIMULATION SUITE FOR MUSCULOSKELETAL MOTOR CONTROL
Vittorio Caggiano (Meta AI Research), Huawei Wang (University of Twente), Guillaume Durandau (University of Twente), Massimo Sartori (University of Twente), Vikash Kumar (Meta AI Research)
https://sites.google.com/view/myosuite/myosuite?authuser=0 https://drive.google.com/file/d/10Le1OmOpy-Veb7n41ywrYLxyipoGfHtt/view
Translated from Des chercheurs de Meta AI et de l’Université de Twente ont développé MyoSuite, une plateforme d’IA qui unifie l’intelligence neurale et motrice